Consumers, aka every individual who participates in the economy, have a rights and responsibilities. Depending on your state and the transaction, you might have a wide range of rights or very few. Believe it or not, with the rise of social media, your most important right might be the “right to complain”!
As a young person, thinking about saving for retirement seems like a world away. However, being able to save enough for retirement means people have to start much earlier than they think.
“Labor” is how much a person works. It is the use of time an exertion of effort to produce something of value. Generally speaking, the more valuable a person’s labor is, the higher their wage.
“Unemployment” is a major economic indicator measuring how much of the working population is currently looking for a job. Just because someone is jobless doesn’t mean they are unemployed – they need to be looking for work!
“Price Controls” are artificial limits that are put on prices. If the limit is put in place to prevent prices from getting too high, they are called Ceilings. If they are in place to prevent the price from getting too low, they are called “Floors”.
Interest rates are a percentage that is used to calculate how much a loan or investment grows over time. A “Nominal” interest rate is just the percentage on the loan – the “Real” rate subtracts expected inflation
Scarcity refers to the fact that resources are finite – people and organizations need to allocate their finite resources between their infinite wants.
“Specialization” is when a labor force begins to divide total production, leading to a rise of experts or specialists. This is called the Division of Labor, and it typically results in much higher productivity of labor.
“Opportunity Cost” is what needs to be given up to get something. This is different from an item’s price – it refers to what you give up in order to get something. The opportunity cost for going to school is that you can’t stay home and nap. The opportunity cost of staying home to nap is not getting your diploma!
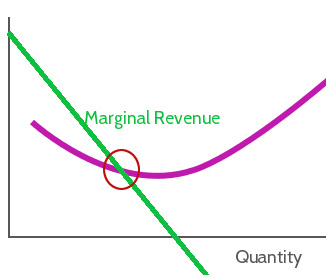
Everyone knows about costs and benefits of doing something – the pros and cons of making a choice. Marginal benefit and marginal cost are different – they look more closely at doing slightly more or less of different alternatives. Marginal costs and benefits are extremely important to producers when choosing their inputs and prices.
Competition occurs in market-based economies, and can be beneficial since it generally leads to lower prices, more choice, and better qualities of products for consumers than other types of economies.
This article describes the Business Cycle, which is the broad, over-stretching cycle of expansion and recession in an economy.
An Entrepreneur is someone who takes a risk to start a new business. Nearly every business that exists (apart those created as spin-offs of other businesses, or by government intervention) was started by one or several entrepreneurs, who took a risk to launch a new company.
Economic Incentives include anything that pushes people, businesses, and governments to do one thing or another. These include what products you buy, what career you choose, what products businesses produce, and what government programs are put in place
In Economics, an “Externality” is a benefit or cost that is not reflected in the price of a good or service. They can be positive or negative.
Economic Growth means that economy is growing – more goods and services are being produced and consumed than they were before. The most common measurement of economic growth is the Gross Domestic Product (or GDP), which measures the total number of finished goods and services produced in an economy in a year.
A “Contract” is a legally binding agreement between two parties (people, companies, or both). Having a contract means that if one party does not keep their word, the other can sue them in court to either force them to fulfill their side of the agreement, or pay back compensation.
Economics studies the trade-offs from a variety of choices. Individuals make these choices everyday, in order to best improve their outcome.
Companies come is all shapes and sizes, with differing levels of liability for its owners. Different types of companies also have different levels of “Liability” – how “on the hook” the owners are for business debt
When someone talks about banking, they generally group together Banks, Credit Unions, and Savings and Loans all in one – but their differences can have a big impact on the services you get!
A Spending Plan is a plan of what you will spend each month, and includes fixed and variable spending. They are used similarly to a budget, but many find them to be more flexible
Money has value because we all agree it has value, and so we can use it as a medium of exchange. Forms of Stored Value simply are a storage system for money like checks and debt cards, meaning they do not have any value in and of themselves.
“Wealth” means having an abundance of something desirable. This can be tangible, like money and property, or intangible.
Financial Records are what you use to have an easy way to tell where all your money and assets are, and exactly how much you have, at any given time. Most people’s financial records will not look the same as anyone else’s, because each person has unique ways of organizing their information to make it most accessible for him- or herself.
A “Fraction” means one piece of a whole, a “Percentage” a calculation that will tell you how big one thing is in relation to another thing, and a “Ratio” is similar to a fraction but used to compare different things. Read this article for more details about these three terms, and how they apply to a portfolio.
In this article we will be looking at how you can use Excel to keep track of your account’s performance. This is meant as a basic guide for people who have little or no experience with Excel.
“Major Economic Indicators” are numbers that you can look at to try to get a picture of how well the economy is doing. This includes GDP, Output, Inflation, Unemployment, and more!
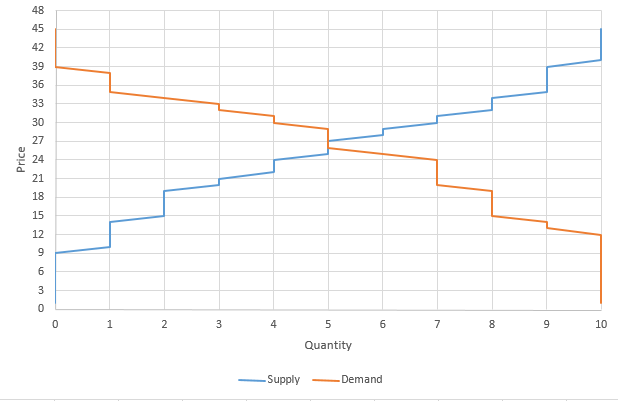
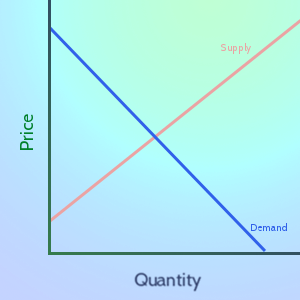
The stock market is the perfect place to see Supply and Demand in action! Many buyers and many sellers meet to trade – with the “market equilibrium” moving in real-time based on new information
In Economics, “Demand” is the relationship between prices and how much people want to buy a good or service.
In Economics, “Supply” means the relationship between prices and production. In general, the higher the market price of a good or service is, the more producers are willing to sell of it.
There are many different economic systems that try to result in more equality or faster growth. The structure of a country’s economy has a lot to do with the country’s politics and the values of its population. However, the economy of every country also changes over time, and how it falls between these broad categories will often change with it.
The Federal Reserve Bank, or the “Fed”, is the central banking system of the United States. It serves as the primary regulator of the US dollar, as well as the “lender of last resort” for other banks.
The Reserve Requirement is how much of all deposits that a bank is required to keep “on hand”, meaning in its vaults, or on deposit at the Federal Reserve Bank (in the United States).
The stock market crash of 1929 was a massive crash in stock prices on the New York Stock Exchange, and marks the largest financial crash in the United States.
In the US, money is created as a form of debt. Banks create loans for people and businesses, which in turn deposit that money in their bank accounts. Banks can then use those deposits to loan money to other people – the total amount of money in circulation is one measure of the Money Supply.
Cottage Industry, or the “Putting Out System”, is a production system of producing goods that relies on producing goods, or parts of goods, by craftsmen at home, or small workshops, instead of large factories. Historically the cottage industry was the major production system for most of human history until the Industrial Revolution.
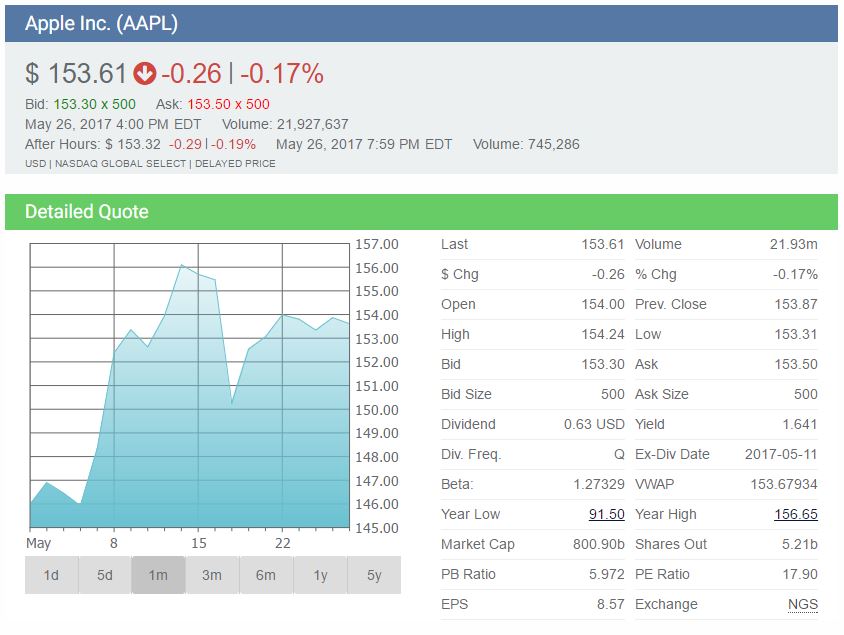
A stock quote represents the last price at which a seller and a buyer of a stock agreed on a price to make the trade. Stock quotes also contain information about the volume, high and low prices of the day and year, and more.
A “Ticker Symbol” is a unique one to five letter code used by the stock exchanges to identify a company.
Stocks are a share of ownership of a company. If you own a stock, you are involved in some of its management decisions, and you are entitled to some of the company’s profits.
The most challenging aspect of starting to invest is picking the first few stocks to add to a portfolio. Every investor has their own techniques and strategies, but we want to give you the tools you need to place your first trades, and get your portfolio off to a running start. Click here for those techniques and strategies.
Mutual Funds come in several different “flavors”, but the core concept is always the same: the fund is a pool of money contributed from many different investors that are used to purchase a bundle of securities. They are professionally managed, so you are basically buying a piece of a larger portfolio.
“ETF” stands for “Exchange Traded Fund”, which is exactly how it sounds; they are like mutual funds in many ways, but they trade on a normal stock exchange like a stock, with their value being determined both by the value of the underlying assets and the value of the ETF itself.
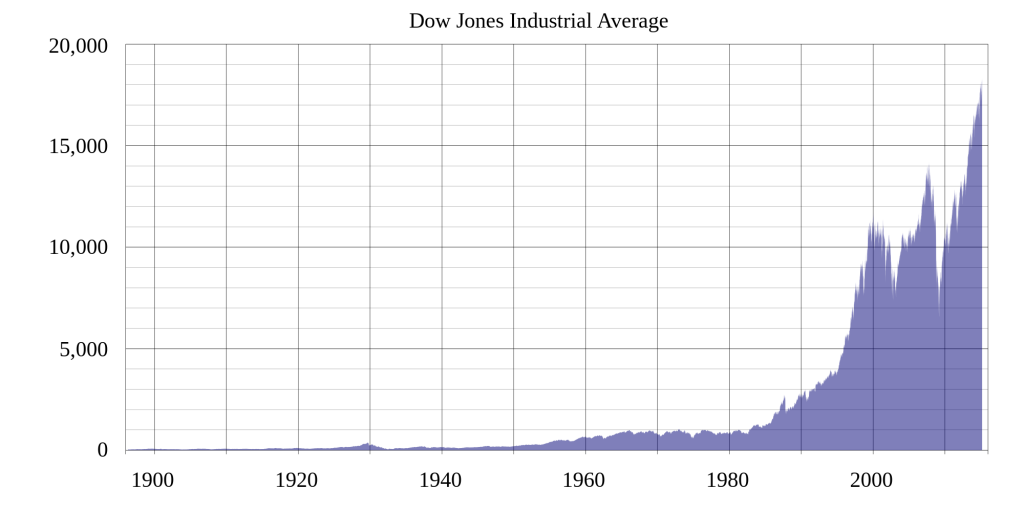
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, more frequently know simply as the Dow or the Dow Jones, is a stock market index made up of 30 of the largest publicly-owned companies based in the United States. It is a price weighted index meaning that the index’s price is an average of the price of the 30 stocks that make it up. Though it is price weighted, this does not mean that every time there is split the index is completely changed, as they have factors to keep the value of the index consistent.
The balance sheet is a financial snapshot of the firm on a specific date – specifically their assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity
The Income Statement is one of the financial statements that all publicly traded companies share with their investors, which shows the company’s sales, expenses, and net profit (or loss) over a period of time–usually 3 months, year-to-date, and twelve months.