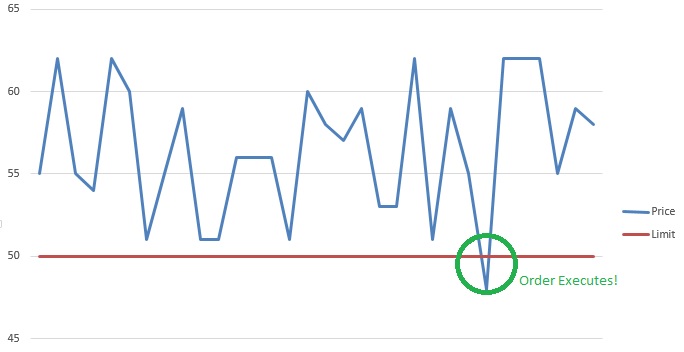
An all-or-none order is an order type that only executes when the full amount of the shares in the order can be executed.
Technical Analysis is the use of technical indicators comprising of statistics using past market information to predict which direction the security price will move. Read this post to learn about the 6 principles that formed the foundation of technical analysis, and some of its purposes and uses.
Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage.
Margin is the amount of money supplied by an investor as a portion of the total funds needed to buy or sell a security, with the balance of required funds loaned to the investor by a broker, dealer, or other lender.
Current Ratio is the ratio of current assets divided by current liabilities. It provides A liquidity ratio that measures a company’s ability to pay short-term obligations. Also known as “liquidity ratio”, “cash asset ratio” and “cash ratio”.
Buy-Side Firms are institutions that provide advice on buying securities and assets within their own organizations.
The Asset/Equity Ratio – the ratio of total assets divided by stockholders’ equity. Higher ratio means each stock has a higher intrinsic worth – regardless of future earnings
Traders, investment firms and fund managers use a trading strategy to help make wiser investment decisions and help eliminate the emotional aspect of trading.
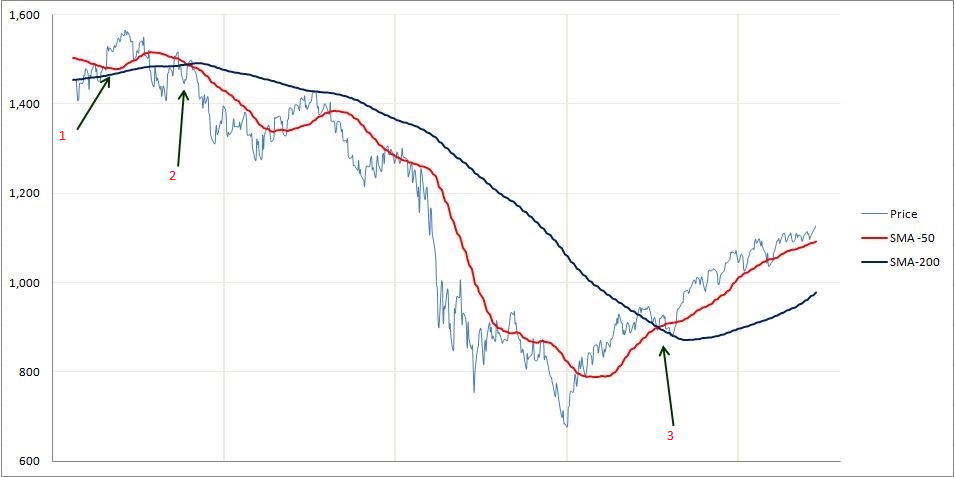
In simple terms, the moving average is an average that compares the previous period over time. There are two types of moving averages: the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) which puts more weight on the latest date.
A dollar Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by that dollar amount.
A zero coupon bond is a bond sold without interest-paying coupons. Instead of paying periodic interest, the bond is sold at a discount and pays its entire face amount upon maturity, which is usually a one year period or longer.
Yield To Maturity is the interest rate that will make the present value of a bond’s remaining cash flows (if held to maturity) equal to the price (plus accrued interest, if any).
Yield is the return investors can expect on a security based on all the outflows and inflows they incur related to that security.
Volume is the quantity of shares/contracts of a security that is traded within a specific time period.
Unsystematic Risk is the risk that is unique to a company such as a strike, the outcome of unfavorable litigation, or a catastrophe that affects its production.
Treasury bills, often referred to as T-bills, are short-term securities (maturities of less than one year) offered and guaranteed by the federal government. They are issued at a discount and pay their full face value at maturity.
A percentage Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage.
Tick refers to a change in price, either up or down.
Strike Price is the price at which an option can be exercised to buy or sell the underlying stock or futures contract.
S&P 500 Index (Standard and Poor’s 500 Index) is a composite of the 500 most actively traded public companies in all ten economic sectors of the U.S. It is maintained by Standard and Poor’s, a division of the Parent company McGraw-Hill.
A Short Sale is a trade in which the investor borrows a security and sells it to another investor in the market.
Security is any financial instrument that represents a financial value.
Recession is generally described as a slowdown of economic growth over a sustained period of time.
Quick Ratio is the ratio that measures the ability of a firm to cover its current liabilities with their most liquid current assets. Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities
A Put Option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying stock or futures contract at a specified strike price.
Pink Sheets refer to the trading of stocks that are not listed on a major exchange or the OTCBB due to a lack of minimum listing requirements or filing financial statements with the SEC (Securities Exchange Commission)
Par Value is the amount that the issuer of a bond agrees to pay at the date of maturity.
Out-Of-The-Money refers to an option that is unfavourable to exercise.
An Options Contract is a contract which specifies how much of the underlying asset can be bought or sold at a specific price. An option contract to buy the underlying is a call option, and to sell the underlying is a put option. Most stock options contracts represent 100 underlying shares.
Market Risk is the general risk for investing in the any security. Every industry in the market is affected by this risk. Examples of market risk: depression, war, inflation etc.
Initial Public Offering, or IPO for short, represents the first opportunity for the public to purchase shares of a company.
Futures Contracts are a standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the end of specified time frame. The price is determined when the agreement is made. Future contracts are always marked to market.
Expiration Date is the last day upon which an option or futures contract can be exercised or traded.
Excess Return is the return in excess of that required by shareholders based on the beta of the company.
Equity is the residual interest of an owner in an asset after all debt and tax payments have been taken care of.
An ECN or Electronic Communication Network is a computer network that facilitates the trading of stocks outside of the regular market hours.
Discount refers to the price of a bond when it is below its par value.
Derivative is a type of security whose value is “derived” from an underlying asset. (Eg; Futures and Options).
A depression is a recessionary decline in real GDP (taking inflation into account) greater than 10% lasting at least 3 years.
Delta is also called the hedge ratio, which is the ratio of the change in price of an option to the change in price of the underlying stock.
Currency Risk is the risk an investor is exposed to when investing in international markets. Currency risk is mainly associated with the fluctuations in exchange rates of the various world currencies.
Coupon Rate is the rate of interest paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the bond’s face value.
A Coupon is the periodic interest payment made to a bondholder during the life of the bond. (Usually semi-annual)
Convertible Preferred Stock are Preferred stock that can be converted into common stock at a particular time frame.
Convertible Bonds are bonds that can be converted into Common Stock usually at the maturity of the bond.
A Contract is term that describes the unit of trading for a stock option, future option or future. It lists all the obligations and particulars related to the security.
Buy-Sell Agreement is an agreement between shareholders or business partners where both parties agree to purchase or sell a stock.
Return on Equity (ROE) is used to measure how much profit a company is able to generate from the money invested by shareholders. Click on this post to see how it is calculated, what kind of ROE you should look for, and more!
EPS (Earnings-Per-Share) measures how much of a company’s net income actually trickles down to each outstanding share. EPS is a good estimator of how much money each shareholder is entitled to from the profits of the company.
PE Ratio (Price-to-Earnings) is a valuation ratio that compares the price per share of a company’s stock to its earnings per share. It basically shows how much investors are willing to pay for a share given the earnings currently generated.