The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME Group) is a publicly-traded derivatives-based exchange (NasdaqGS: CME), and is currently the largest futures exchange in the world in terms of number of contracts outstanding (or open interest).
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) is a publicly-traded exchange (NYSE: BOT) that specializes in futures and options trading. It is highly active in markets such as agriculture, energy, equities, and US Treasuries, providing an important risk-management function for thousands of its CBOT members.
Cash Conversion Cycle is defined as the length of time (in days) needed to transform inventory purchases into actual cash receipts. It takes into consideration the company’s time commitment towards collecting receivables and paying its suppliers, and is an important measure of a company’s internal liquidity.
Capital funding is the provision of monetary resources or capital for productive uses. Capital provided by investors or other parties is used by various entities such as governments, companies, organizations, and individuals in order to fund their functions and operations.
Account Receivables Management refers to the set of policies, procedures, and practices employed by a company with respect to managing sales offered on credit. If efficient, receivables management can lead to good sales growth, healthy cash flows, profitability, and stable operating cycles.
Account Payables Management refers to the set of policies, procedures, and practices employed by a company with respect to managing its trade credit purchases. It is an important working capital amount that can enhance a company’s short-term cash flow position.
The idea behind insurance is that there are random bad – and expensive – things that happen to just about anyone. Car crashes, medical emergencies, and other problems that can destroy your personal saving and investing plans if they happen. To protect against this, insurance companies work to pool the resources of many people together in one group.
A Commercial Bank, also known as Retail Banking, is a type of financial institution that is responsible for catering to everyday banking needs. This is the kind of bank that individuals go to for their everyday financial needs.
Once you have chosen your investment strategy it is time to start building your stock portfolio. Your strategies should be inline with your overall investment strategy such as whether you are day trading and the level of risk you are looking for. Click on this post for some strategies!
A portfolio is a collection of assets that contribute collectively to an overall return. There are many different reasons you could create a portfolio, and you need to define your reason or objective from the very beginning before adding stocks and other securities to your account. This will give a description of potential objectives a portfolio could have, as well as descriptions of potential assets you can choose.
A price ceiling is a government-mandated limit on the price that can be charged for a given product, such as a utility or electricity. The intended purpose of a price ceiling is to protect the consumers from conditions that would make a vital product from being financially unattainable for consumers.
A “Poison Pill” is a way to give shareholders more time to evaluate a hostile takeover bid and to give management the opportunity to make better informed business decisions. It was created in the 1980’s, a period rife with hostile takeovers and corporate raids.
A straddle is an investment strategy that involves the purchase or sale of an option allowing the investor to profit regardless of the direction of movement of the underlying asset, usually a stock. Read this article for details on the two straddle strategies: a long straddle and a short straddle.
An oligopoly is characterized by a small number of sellers who dominate an entire market. All of the firms who partake in an oligopoly are considered to be very large in terms of profit, size and client base.
Monopoly, in economic terms, is used to refer to a specific company or individual has a large enough control of a particular product or service that allows them to influence it’s price or certain characteristics.
Monopolistic Competition is characterized as a form of imperfect competition, which exist when there are many sellers of a good or service but the products do not contain noticeable differences. There are several forms of imperfect competition, of which Monopolistic Competition is one.
Money supply is the total amount of money available in an economy at any particular point in time. Money is required for both consumers and businesses to make purchases. Money is defined as currency in circulation and demand deposits (funds held in bank accounts.)
Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) is an investment theory whose purpose is to maximize a portfolio’s expected return by altering and selecting the proportions of the various assets in the portfolio. This article discusses the assumptions of MPT, and its limitations.
The Expected Return is a weighted-average outcome used by portfolio managers and investors to calculate the value of an individual stock, or an entire stock portfolio.
A Portfolio Manager is a professional investment adviser that manages a client’s assets. They should be registered with an investment authority and be certified to act as a manager. Read this post for details on how to evaluate a portfolio manager.
Economists define elasticity as the ratio of the percent change in one variable to the percent change in another valuable. Its purpose is to measure how one variable responds to changes in another variable.
Duration measures the percentage change in the price of a bond (or value of a bond portfolio) due to a change in market interest rates (also known as the yield).
Return on Equity (ROE) is one of the most important pieces of data that investors and creditors use to evaluate a company’s potential to grow and profitability. Dupont Analysis breaks the ROE into several different components in order to analyze where the returns are coming from.
The Direxion Small Cap Bear 3x is a triple-leveraged ETF offered by Direxion Investments that seeks to negatively triple the returns of the Russell 2000 stock index.
Straight line depreciation is the most commonly used and simplest form of depreciation.
Depreciation refers to the gradual and permanent decrease in value of the assets (referred to as a depreciatable asset) of a firm, nation or individual over its lifetime.
The consumer price index (CPI) is simply an indicator of changes in prices of goods and services experienced by consumers in a given country over time.
A basic material used in manufacturing or commerce that is interchangeable with other the same commodities coming from a different source. The quality of a specific commodity may differ slightly, but it is essentially uniform across producers. When they are traded on an exchange, commodities must also meet specified minimum standards, also known as a basis grade. Typical types of commodities are corn, gold, silver, steel, etc.
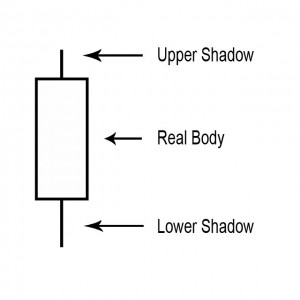
The body of the candlestick chart is the most basic building block for a candlestick chart. Read this article to learn more!
A point on a candle stick chart representing a specific time period (a day, an hour, a minute, etc) in which the underlying stock price has moved. Candlesticks will have a body and usually two wicks – one on each end.
A shadow is the small line (like a candle wick) found at the top or bottom of an individual candle in a candlestick chart.
An investment strategy that aims to capitalize on the continuance of existing trends in the market. The momentum investor believes that large increases in the price of a security will be followed by additional gains and vice versa for declining values.
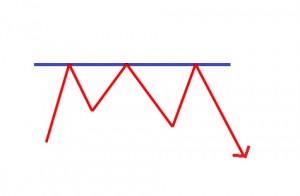
The Resistance Line is a point or range in a chart that caps an increase in the price of a stock or index over a period of time.
The price-to-sales ratios (Price/Sales or P/S) take the company’s market capitalization (the number of shares multiplied by the share price) and divide it by the company’s total sales over the past 12 months. The lower the ratio, the more attractive the investment.
Stagflation is high inflation and high unemployment are occurring simultaneously.
Inflation-Indexed Securities are securities with a guarantee of a return rate that is higher than the rate of inflation if it is held to maturity.
The fee charged by a broker or investment advisor in exchange for investment advice and/or handling the purchase or sale of a security. Commissions vary from brokerage to brokerage.
Earning estimates are an estimate of forecasted earnings and they provide one strong measure of potential future performance and are a mainstay of stock investing research!
This post describes, Return on Equity (ROE), which is used to measure how much profit a company is able to generate from the money invested by shareholders.
Price/Earnings To Growth, is a valuation metric for determining the relative trade-off between the price of a stock, the earnings generated per share (EPS), and the company’s expected future growth. It can be useful when looking at the future earning growth.
The question of when to sell stocks is not easily answered, but this post ventures to give a description of how to know when it’s time to sell!
Stock volatility information can be used in many different ways but here is a quick and easy bit of stock volatility information that you can begin using today.
There is very little information available about how to handle the stocks you already own, but knowing Stock Exit Strategies is essential for minimizing your losses and protecting your portfolio. Read this article for information on Stock Exit Strategies.
The golden rule of stock investing dictates cutting your losses when they fall 10 percent from the price paid, but common wisdom just might be wrong. Instead, use some common sense to determine if it’s time to hold or fold.
The typical hedge fund is designed to be a partnership arrangement with the fund manager acting as the general partner responsible for making investment decisions, and is one of the investment tools serious investors aspire towards.
Buying what you know takes advantage of your familiarity with a product or market and translates that knowledge into potential earnings. Think of it this way; good investors understand opportunity and risk. Read this article to learn more!
Small cap stock investing is volatile. So, why risk your money by investing in what is typically considered risky business?
Hyperinflation refers to out of control or extremely rapid inflation, where prices increase so quickly that the concept of real inflation becomes meaningless. The classical definition of hyperinflation is inflation greater than 50% per month.
Inflation refers to the general rising of prices for goods and services in the economy, due to an increase in the amount of money and/or credit available. When it occurs, the purchasing power of your dollar falls.
A CD or Certificate of Deposit is one of the safest and liquid forms of investment available. Insured by the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation), CDs are a type of interest earning deposit account.